Health Professionals:
Folic Acid and NTDs
During embryonic development, the neural plate undergoes a change in shape to create an infolding and closure to form the neural tube, the structure that develops into the brain, spinal cord and spine. Neural tube closure occurs between 22 and 28 days after conception. When the neural tube does not form correctly and does not completely close, a serious birth defect can develop called a neural tube defect (NTD). NTDs occur very early in pregnancy, even before most women know they are pregnant.
These serious malformations--which include spina bifida, anencephaly, and encephalocele--are among the most commonly observed birth defects in humans and are a major cause of infant mortality and serious disability.
Spina Bifida
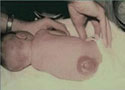 Spina bifida is the most common NTD and occurs when the spinal column fails to close completely during early development, allowing the spinal cord to be exposed and open to possible damage.
Spina bifida is the most common NTD and occurs when the spinal column fails to close completely during early development, allowing the spinal cord to be exposed and open to possible damage.
- Spina bifida may cause leg paralysis, bladder and bowel problems, hydrocephalus, and/or other serious health complications.
- The severity of the disability depends on the size and location of the opening on the spine. Usually, the larger defects and those higher on the spine cause more disability.
- Children born with this condition usually need surgery in the first few days of life to close the defect.
- Most people with spina bifida need to use a wheelchair or leg braces throughout their life.
Anencephaly
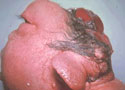 Anencephaly is an incomplete or severely underdeveloped skull with the brain partially or completely absent.
Anencephaly is an incomplete or severely underdeveloped skull with the brain partially or completely absent.
Unfortunately, this birth defect is always fatal with death occurring before birth or shortly thereafter.
Photo courtesy of Virginia Commonwealth University, Department of Pathology, Neuropathology mini-course website. Used with permission.
Encephalocele
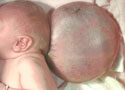 Encephalocele is an opening in the skull that allows some of the brain to protrude outside the skull, covered only with a membrane (meninges).
Encephalocele is an opening in the skull that allows some of the brain to protrude outside the skull, covered only with a membrane (meninges).
Depending on the severity of the defect, encephalocele can result in varying degrees of mental disability or may be fatal.
Photo courtesy of Virginia Commonwealth University, Department of Pathology, Neuropathology mini-course website. Used with permission.

Neural tube defects affect approximately 3,000 pregnancies per year in the U.S.
It is important to note that approximately 95% of children with an NTD are born to couples with no family history of these defects. For those couples who have had a previous child with an NTD, the risk of recurrence is essentially tripled for each subsequent pregnancy.

